The Security Broker Service: How to Manage the Access to Production Data on the TRICK Platform

TRICK platform will provide a wide range of services, accessible to different types of stakeholders at different stages of confidentiality. In this context the platform architecture, including the skeleton to support both core and business services, cannot miss the security aspects. Therefore, a crucial role is played by the implementation of a component for orchestrating the security related to the access and management of the stored data (e.g. Blockchain infrastructures and databases).
The activity was led by Domina that firstly analysed and defined the security aspects at a design phase, following the principle of privacy by design (Task 2.1) and secondly handled the implementation of the Security Broker as a fundamental component to provide all the full security functionalities required for the platform services. This second step was addressed in the Task 2.4 – Secure data access and management, in which the aspects and functions of the Security Broker and the approach used for its development were defined.
Security broker in TRICK: aspects and functions
Security Broker is a core service of TRICK, it regulates the access to production data, assuring the management of authentication, authorization, confidentiality and privacy. It offers the following functions, by means of a set of RESTful APIs:
- authentication of users and services
- authorization of users and services
- privacy/confidentiality of data at rest
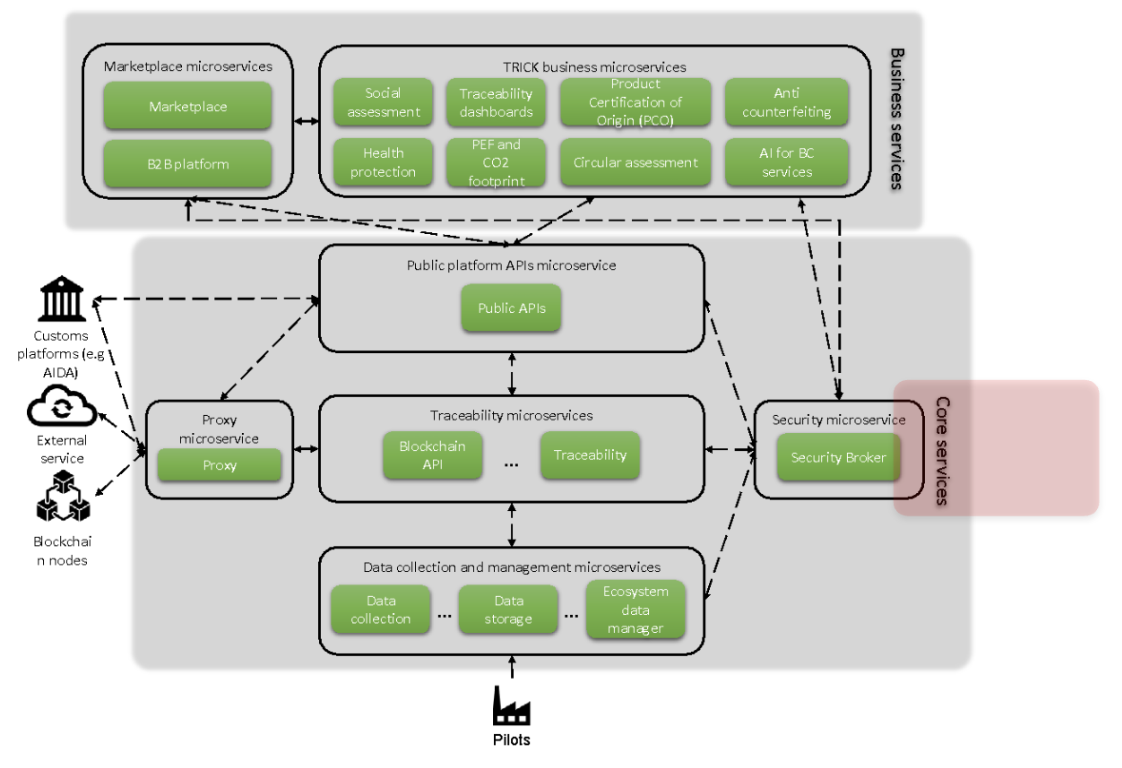
Security Broker in TRICK platform architecture
Security Broker in TRICK platform architecture
Let us go into more detail and explore how Security Broker handles its three main functions:
- Authentication of users and services (i.e. the capability to identify a user or service by using a set of credentials) is the first step for accessing a platform and, therefore, it’s critical. Several existing frameworks and libraries are available, the approach is to adopt a well-designed and market-ready open-source software to guarantee the correct and secure implementation of authentication;
- Authorization of users and services, can be defined as the capability of evaluate which actions (e.g. read, write) can be performed on a resource (e.g. document) for a particular user/service. It requires a policy model to define the rules for relate users, resources and actions. Also in this case, the adoption of well-known approaches and existing software components is useful;
- Privacy/confidentiality of data at rest, (i.e. the capability of encrypt/decrypt data at rest on-demand): generally, an information can be public or private, in the second case, to guarantee its confidentiality the encryption is exploited. Therefore, Security Broker must address this functionality offering it to core and business services.
Authorization and policy model: how to define the relations among users, resources and permissions
In order to define and organise the relationships among users, resources, (e.g. document, service, information) and permissions (e.g. read, write, delete, create) it is required to adopt a policy model. Several approaches have been proposed in the last few years, among them the RBCA model limits the number of policies to be written, with an effective evaluation without inserting latency on the policy decision process. It is a positive advantage, however, this approach in TRICK’s context is not adequate, because it does not allow to represent special permissions, in other words the possibility, for a user to perform a particular action on a resource that is not strictly related to a role. To overcome the limitation of RBCA in the management of policy exceptions, the ACL - Access Control List was adopted. With ACL a policy can define the user’s option to perform a specific action on a specific resource or a group of resources avoiding belonging to a strict role. As a consequence this approach requires to define a policy for each exception and therefore, to be effective, must be engineered correctly.
Authentication and authorization in few steps
The authentication and authorization approach can be summarized in the following 3 steps, useful for verifying if and how a user can proceed to access a requested permission:
- authentication of the user
- release of a JWT token for the access
- finally, the authorization module is responsible for checking user’s permissions
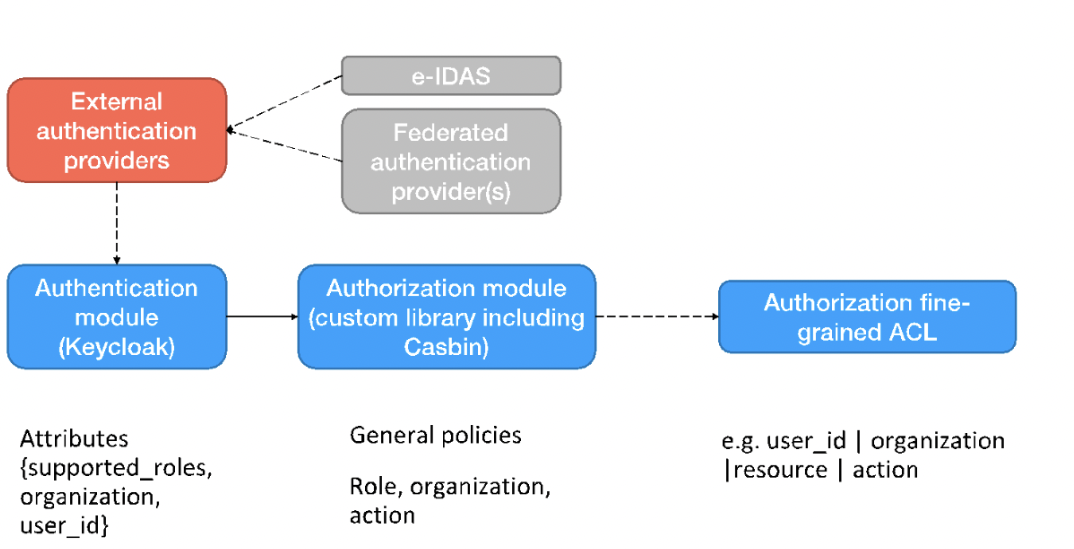
The approach for providing authentication and authorization
That's how the procedure is addressed in detail:
Firstly, a user must be authenticated, in other words his/her credential must be checked. Therefore, he/she can perform login with credential by using:
- Security Broker and its internal Keycloak (https://www.keycloak.org/) component
- or by using an external Identity Provider, for example, e-IDAS or other federated providers: in this case, the external Identity Provider interacts with TRICK Keycloak to generate a user certificate with verified attributes that can be used later on for authorization purposes (i.e. ABAC)
Second, once the authentication succeeded, a JWT token, containing user’s information and related attributes (useful for authorization) is released. This token will be employed by the user to access services and resources.
Third, a specific authorization module extracts user’s information and attributes (e.g. organization, supported role) from token, resource and action from user’s or service request, to evaluate whether exists a general policy that permit the action by considering supported roles, organization, and resource.
In case of success, the operation on the resource is granted. If it does not exist a general policy to grant access to the user, the authorization module evaluates the fine-grained ACL policies to find whether exists a policy for this exception. In case of success, the access is granted, otherwise the access is denied.
The confidentiality engine: procedures for encryption and decryption
As already mentioned, Security Broker also deals with confidentiality procedures, including encryption and decryption of data at rest, modulated by the related user access policies. The Confidentiality engine works as showed in the figure below. More precisely for the encryption:
- a resource encryption request starts the process
- the confidentiality engine generates, in a random way, a key (256 bit) and a IV (Initialization Vector)
- then it stores key and IV into Vault (https://www.vaultproject.io/), indexed by resource identifier
- finally, it performs the encryption and returns encrypted byte
Similarly, for the decryption, the process works as follow:
- a resource decryption request starts the process
- the confidentiality engine retrieves from Vault, a key (256 bit) and a IV (Initialization Vector) by using resource identifier
- finally, it performs the decryption and returns clear bytes
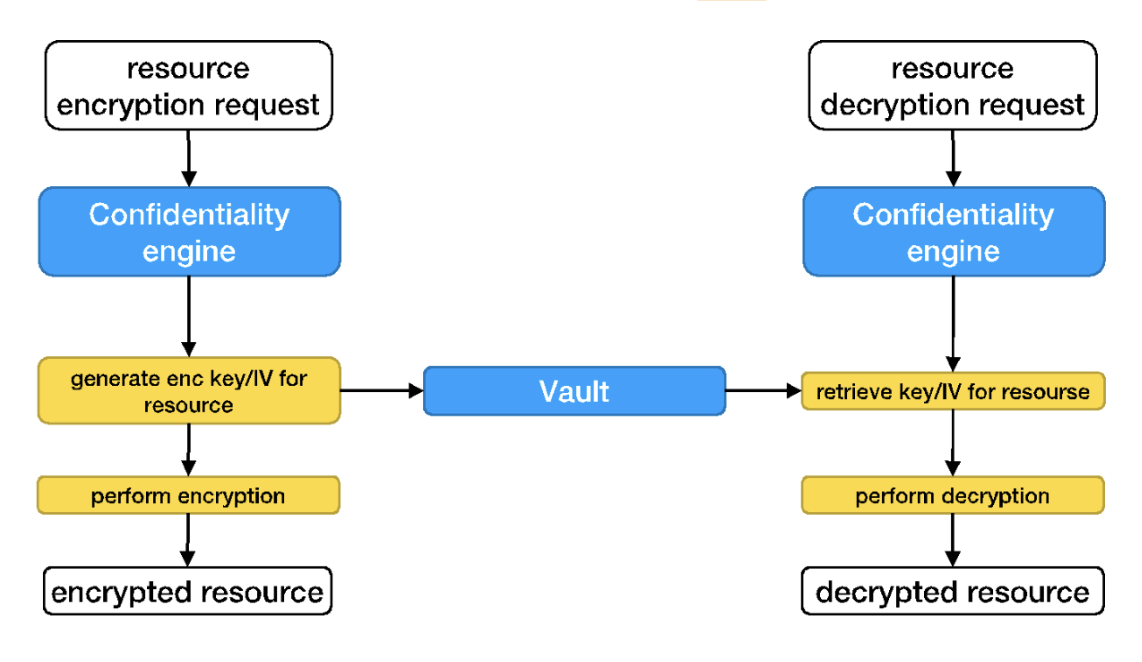 Confidentiality engine
Confidentiality engine
CONTACT PERSON & EMAIL ADDRESS:
- Stefano Fasana (email)
LINKS:
- Domina (Website)